Risky driving highest at beginning and end of shifts, Samsara finds
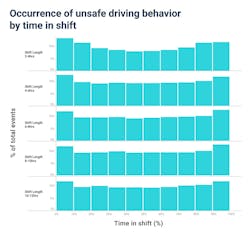
Compared to the middle of their shifts, commercial drivers are 26% more likely to exhibit unsafe driving than at the start and 41% at the end of their shift, according to data gathered by Samsara’s telematics platform and analyzed by the company.
Samsara used four metrics for the analysis: harsh acceleration and harsh braking (measured by g-force); and distracted driving and tailgating (determined by artificial intelligence). Since Jan. 1, 2020, 2 million such events were detected in U.S. commercial fleets.
Shift lengths ranged from four to 12 hours, but these unsafe trends appeared consistent throughout, Samsara noted.
One stat that jumps out is harsh acceleration occurs 77% more often during the last 1/10th of shift than in the middle. That’s nearly double the frequency at the beginning of a shift relative to the middle (39%). Harsh braking has similar results, with 54% more likely at the end versus 28% at the beginning.
Conversely, distracted driving is 36% more likely during the first part of the shift, which is twice as much as at the middle-to-end difference.
At least three factors are believed to contribute to the skewed results at the start and stop of a shift:
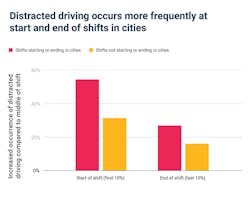
- Increased traffic in cities: Moving from local roads to highways (and vice versa) occur more frequently at the onset or tail-end of a shift, and there are more opportunities for distraction and traffic in these areas.
- Last-mile stops: "Our data shows there are more short trips (likely due to deliveries and last-mile stops) at the beginning and end of shifts, causing drivers to stop and start more frequently, which can create more opportunities for unsafe driving behavior," Samsara explained
- Driver fatigue: Seven hours of sleep per night is recommended, though 37% of the workforce does not hit that goal. That grogginess could dull reactions on the road at the start of shift. And at the end of shift, fatigue can creep in.
By receiving an in-cab alert about harsh braking and accelerating, drivers reduced this risky behavior by 40%. Other actions that Samsara said would be effective to curb risky behaviors include sharing this new data in safety meetings or company electronic communication, as well as providing data to a driver during a coaching session to reinforce the safety trainer’s mentoring. The combination of anecdotes and hard evidence has been found to boost memory by as much as 22 times versus spitting facts alone, according to the late psychologist Jerome Bruner.
About the Author
FleetOwner Staff
Our Editorial Team
Kevin Jones, Editorial Director, Commercial Vehicle Group
Josh Fisher, Editor-in-Chief
Jade Brasher, Senior Editor
Jeremy Wolfe, Editor
Jenna Hume, Digital Editor
Eric Van Egeren, Art Director